
The largest expansion will come from hydroelectricity, which is expected to be expanded to 120 GW. China also has plans to expand their renewable generation. The 12th Five Year Plan dictates that 40 GW will be installed by 2015. China will also include nuclear generation in their expansion plan. China has plans to build nine new coal plants by 2015. Coal and petroleum currently represent the vast majority of China's generation mix and this trend will continue with their generation expansion plan. China's third area of focus is on reducing the environmental impact of their electricity generation sector.Ĭhina is a pursuing an all of the above strategy to fulfill their generation needs. The second focus area correlates with expanding generation and focuses on expanding China's electricity transmission and distribution systems. The first focus area is on expanding generation, to address the explosive growth of electricity demand over the last 20 years which is expected to continue. Asia China Ĭhina's Smart Grid efforts are focused on three key areas. The 2013 IRP identified five transmission line corridors that would be needed to help connect new generation to demand centers. To address the final objective of improving network reliability and availability South Africa plans to expand their transmission and distribution grids. Improve Network Reliability and Availability The goal of either mechanism would be to keep the emissions from electricity generation between 95 – 193 million tons per annum (MT/a) by 2050.

The third strategy being considered is an emissions cap, carbon tax, or carbon budget.
#SMART GRIDS UPDATE#
The 2013 South Africa Integrated Resource Plan Update (IRP) projected that 800 MW of co-generation, 2.37 GW of combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) and 3.9 GW of open cycle gas turbine (OCGT) would be built by 2030. The second strategy involves increasing their gas generation.

The first is incorporating more renewable generation though the IPP energy auctions discussed above. To achieve the objective of decarbonizing their electricity generation South Africa is employing three strategies. As of 2013, 2.47 GW of renewable capacity had been contracted. The independent power producers (IPP) can bid anywhere between 1-75 MW and winners receive their bidden rate for 25 years. Eligible technologies include onshore wind, solar thermal, solar PV, biomass, biogas, landfill gas, and small hydro. To achieve the objective of increasing renewable generation, South Africa began hosting renewable energy auctions in 2010. Increasing Penetration of Renewable Generation South Africa has Smart Grid efforts are focused around three objectives: increasing the penetration of renewable generation, decarbonizing their electricity generation and improving network reliability and availability.ġ. 4.1.2 Smart Meter rollout in member nations and transition to smart grid.
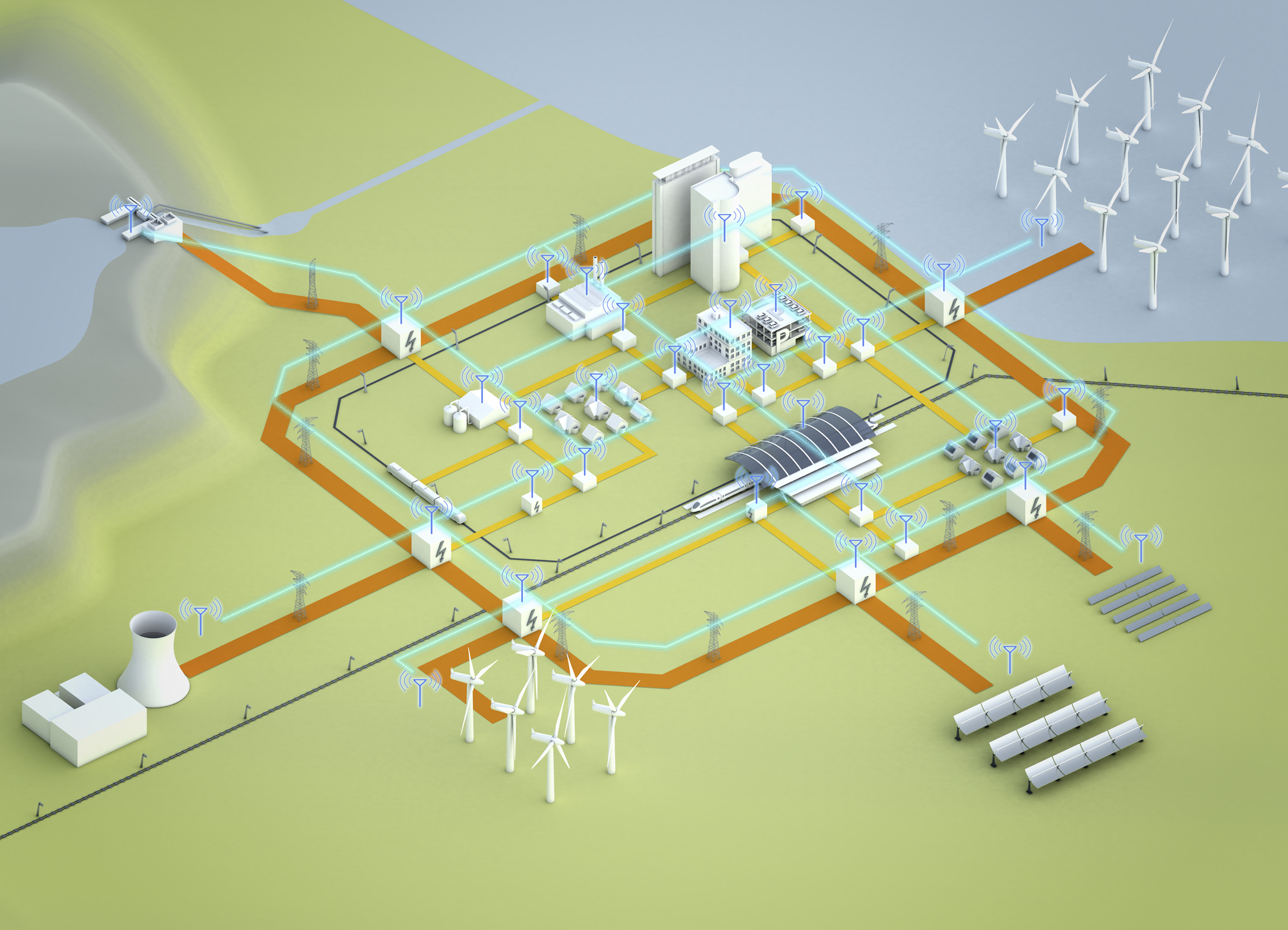
4.1.1 The concept of Smart Grids in Europe.Department of Energy (DOE), and other organizations representing various community interests. In addition, NIST engages with many stakeholders in the electricity sector through its interactions with the Smart Electric Power Alliance (SEPA), the U.S. The program draws on expertise from across the breadth of the NIST organization. This program advances the measurement science necessary to increase asset utilization and efficiency, improve grid reliability, and enable greater use of renewable energy sources in the grid through research, standardization, testing, and implementation of the NIST Framework.
#SMART GRIDS FULL#
In addition, we are conducting a full cycle of research, development, and innovation that provide the foundations for the future grid. Working with stakeholders and partners from industry, government, and academia, we’ve built a solid framework and roadmap for smart grid interoperability standards including current work toward Release 4.0. A modernized grid enables all participants to benefit from the new introduction of new technologies, from distributed resources to advanced communications and controls. Leveraging NIST’s century-long partnership with the electric industry, we are collaborating with our partners to address this generation’s grand challenge-modernizing the electric power grid so that it incorporates information technology to deliver electricity efficiently, reliably, sustainably, and securely.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
